December 22, 2025 – A new study—led by Dr. Yael Heifetz and Dr. Alisa Komsky-Elbaz, along with Margarita Shuhmaher and Dr. Javier Arturo Sanchez-Lopez at Hebrew University, in collaboration with Prof. Yoav Soen of the Weizmann Institute of Science and Dr. Amir Hefetz from DatGraph, and published in The Journal of Extracellular Vesicles—uncovers a previously underappreciated communication network between the early embryo and the uterus, which may be critical for successful implantation and early pregnancy. The study reveals how extracellular vesicles, lipid droplets, and aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) ligands dynamically interact during the earliest stages of embryo-maternal crosstalk.
Understanding one of the most fragile stages of pregnancy
Implantation is one of the most delicate and failure-prone stages of pregnancy in humans and other animals. Despite its importance, the molecular language that enables an embryo to signal its presence and coordinate with the maternal endometrium remains incompletely understood. Using a human in vitro co-culture model, the Heifetz team examined how cells exchange signals during the window of implantation (WOI), a short, hormonally regulated phase in which the uterine lining becomes receptive, and implantation can take place.
“Our findings show that implantation is not a passive process,” the researchers said. “The embryo and the uterus are engaged in an active, highly coordinated dialogue mediated by extracellular vesicles. These vesicles allow the transfer of signals and metabolic information that help both tissues adapt to the rapidly changing demands of early pregnancy.”
Tiny vesicles as information carriers
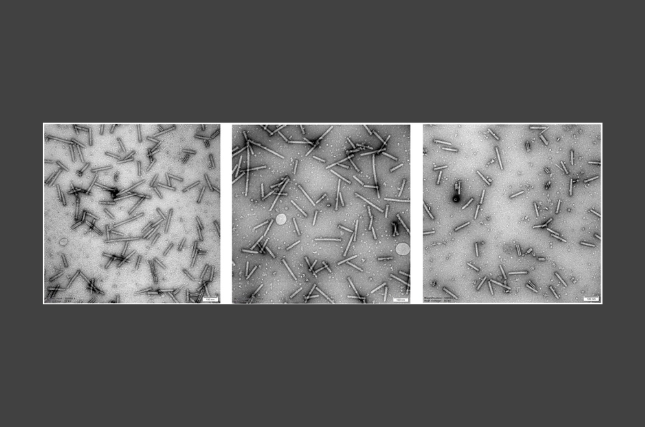
The study focuses on extracellular vesicles, which are small, membrane-bound packages released by cells that share information and materials, a bit like parcels sent between neighbors. The team found that hormonal stimulation occurring during preparation of the uterus for implantation alters the extracellular vesicles released by the uterine lining, producing distinct extracellular vesicle populations that differ in size, release rate, uptake efficiency, and molecular content.
Lipid droplets – more than energy storage
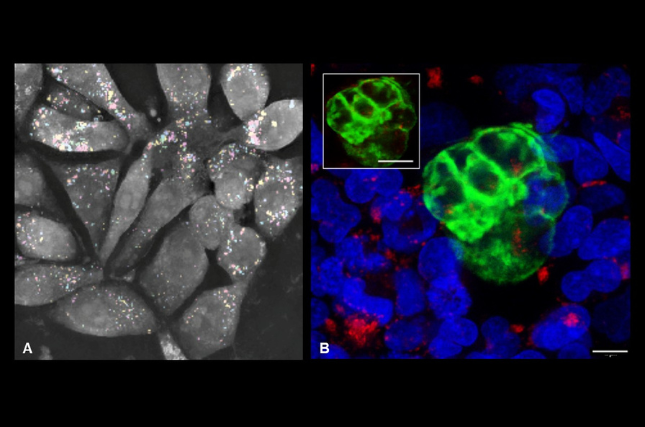
The team identified lipid droplets as active participants in embryo-maternal communication, rather than passive energy reservoirs. Lipid droplets, which store fats and energy inside cells, are influenced by both endometrial- and embryo-derived extracellular vesicles and are actively transferred to embryonic cells, contributing to implantation-related processes. Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of lipid-related molecules reshapes lipid droplet dynamics in recipient cells, suggesting a tightly regulated metabolic adaptation during implantation.
“Lipid droplets emerge as functional hubs that integrate metabolic and signaling inputs during implantation”, the researchers explained. “This challenges the classical view of lipid droplets, and places cellular metabolism at the heart of embryo-maternal communication.”
AhR ligands link environment, metabolism, and reproductive success
A key discovery of the study is the involvement of AhR ligands, signaling molecules known to respond to dietary and environmental cues. The findings indicate that extracellular vesicles selectively carry energy-related metabolites and AhR ligands. Furthermore, inhibition of AhR signaling significantly increased the attachment of embryo-like spheroids to uterine cells, indicating that this pathway plays a regulatory role in implantation, placing AhR at the crossroads of environmental sensing, metabolism, and reproductive success.
“Our data indicate that AhR signaling fine-tunes the implantation process and provides a mechanistic explanation for how external and internal environmental factors may influence fertility at its earliest stage,” the researchers added.
A two-way functional exchange
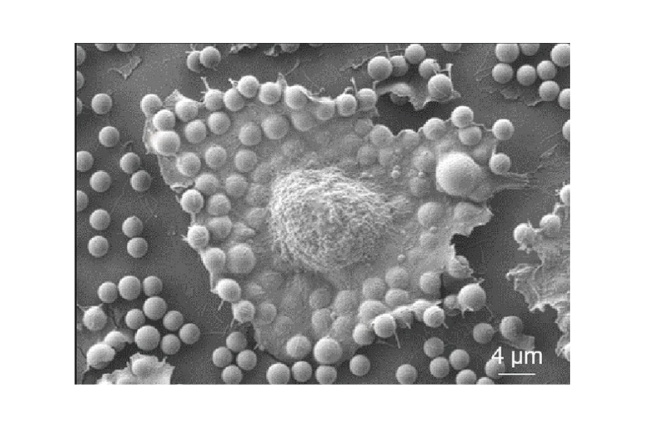
The study also shows that communication is not one-sided. Extracellular vesicles are exchanged between the embryo and the endometrium and are rapidly taken up, typically within about an hour. extracellular vesicle-derived mRNA was shown to be translated soon after uptake, driving cellular changes that support embryo attachment. Once internalized, these vesicles can influence how cells produce energy, process lipids, and surrounding tissue are remodeled.
A model for studying early implantation
The model used in this study provides a useful platform for examining how EV-mediated two-way communication shapes early embryo-maternal interactions. The work helps clarify how the embryo and endometrium influence each other at very early stages. This system can also be used to study similar extracellular vesicle-based communication in other biological settings.
The findings contribute to a more detailed understanding of how extracellular vesicles, extracellular metabolites, and lipid droplets act together to promote embryo attachment and implantation, and may inform future research in reproductive biology and fertility.
The research paper titled “Extracellular Vesicles, Lipid Droplets and AhR Ligands in Early Implantation: The Dynamics of Embryo-Maternal Crosstalk” is now available in J Extracell Vesicles and can be accessed here.
Researchers:
Alisa Komsky-Elbaz1, Margarita Shuhmaher1,2, Javier Arturo Sanchez-Lopez1, Oria Teena1, Daniel Waiger3, Einat Zelinger3, Tally Kossovsky3, Leilah Otikovs4, Eshel Dilevsky5, Yoav Soen6, Amir Hefetz7, Yael Heifetz1
Institutions:
- Department of Entomology, The Hebrew University, Rehovot, Israel.
- Current Address: Biomedical Engineering, Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel.
- Center for Scientific Imaging, The Hebrew University, Rehovot, Israel.
- Sciences Core Facilities, Weizmann Institute, Rehovot, Israel.
- Markel Technologies Ltd., Yehud, Israel.
- Department of Biomolecular Sciences, Weizmann Institute, Rehovot, Israel.
- DataGraph, Holon, Israel.